Preparation for the Adoption of AI Operators in Companies
- Marcos Recolons
.png/v1/fill/w_320,h_320/file.jpg)
- Mar 17
- 3 min read
AI operators are autonomous agents capable of performing tasks in graphical user interfaces (GUI) by simulating human actions, such as keyboard and mouse manipulation. Their implementation requires detailed planning regarding data collection, process restructuring, and compliance with security and governance standards.
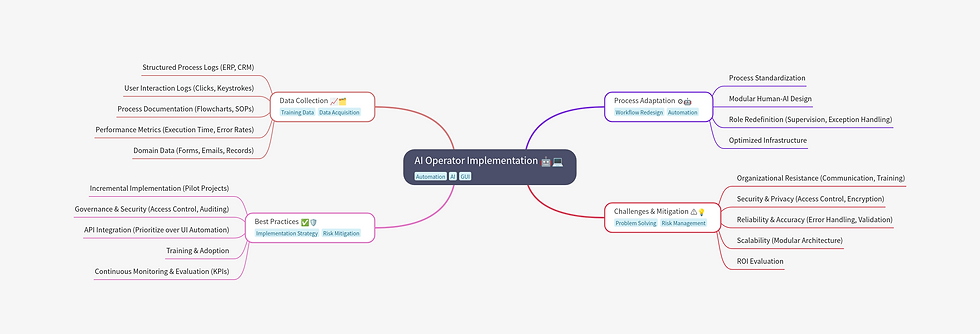
1. Data Collection for Training and Configuration
To train AI operators, it is essential to gather structured and unstructured data that reflect business operations:
Structured process records: ERP and CRM logs with transactional details, timestamps, and user activity.
User interaction logs: Captures of actions in the interface (clicks, keyboard events, and UI changes).
Process documentation: Flowcharts, standard operating procedures (SOPs), and technical manuals.
Performance metrics: Execution times, error rates, and bottlenecks identified in repetitive tasks.
Domain data: Structured and unstructured datasets with which AI will interact (forms, emails, historical records).
Recommendation: Implement log capture and task mining tools to obtain granular traceability of processes.
2. Process Adaptation for AI Integration
The adoption of AI operators requires adjustments in workflow architecture:
Process standardization: Streamline workflows and reduce variations to optimize implementation.
Human-AI modular design: Define tasks for full automation, partial automation, or user assistance.
Role redefinition: Shift human activities toward supervision and exception resolution.
Optimized infrastructure: Ensure computational resources and controlled environments for AI agent execution.
Recommendation: Conduct process audits and define hybrid architectures with well-defined human intervention points.
3. Best Practices for Implementation
To minimize risks and ensure a smooth transition, best practices should be followed:
Incremental implementation: Deploy pilots in limited processes before scaling.
Governance and security: Establish access policies, auditing, and credential management.
API integration: Prioritize system interconnection via APIs rather than UI-based automation.
Training and adoption: Train teams in usage, supervision, and maintenance of AI agents.
Continuous monitoring and evaluation: Define efficiency KPIs and error rates for model optimization.
Recommendation: Establish an automation office to document policies, methodologies, and continuous improvements.
4. Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
AI operators present technical and organizational challenges that must be anticipated:
Organizational resistance: Implement communication and training strategies to minimize friction.
Security and privacy: Apply role-based access control, data encryption, and continuous auditing.
Reliability and accuracy: Design failover mechanisms and validation processes for automated outputs.
Scalability: Develop modular architectures to facilitate AI operator expansion and updates.
ROI evaluation: Measure impact on operational efficiency and long-term maintenance costs.
Recommendation: Maintain a risk log and apply iterative strategies to address deviations.
Conclusion
The adoption of AI operators requires changes in technology, processes, and organizational culture. To ensure an efficient implementation, a solid strategy must be in place, considering data collection, workflow optimization, and a rigorous approach to governance and security. A well-structured deployment will maximize AI’s impact on automating repetitive tasks, improving operational efficiency, and reducing errors. Proper preparation and continuous improvement will ensure adaptability and scalability of these systems over time.
Sources: Hyland (2023). “Preparing your business for RPA and AI integration.” – Hyland.com HYLAND.COM HYLAND.COM IBM (2022). “The Types of Process Mining (Task Mining vs System Logs).” – IBM Think Blog IBM.COM IBM.COM Visionet (2019). “How RPA is changing your role in the workplace.” – Visionet Blog VISIONET.COM VISIONET.COM Trigyn (2024). “Best Practices for RPA Implementation.” – Trigyn Insights TRIGYN.COM TRIGYN.COM SolveXia (2023). “6 Key RPA Challenges and How to Overcome Them.” – SolveXia Blog SOLVEXIA.COM SOLVEXIA.COM Inside Small Business (2019). “Study reveals employees to benefit most from RPA adoption.” INSIDESMALLBUSINESS.COM.AU INSIDESMALLBUSINESS.COM.AU Nash Tech (2021). “RPA adoption leads to 57% reduction in data entry process times (Tradetech case study).” NASHTECHGLOBAL.COM Automation Anywhere (2023). “What is Process Mining & How Can It Automate Workflows?” AUTOMATIONANYWHERE.COM (explaining use of event log data)



Comentarios